Gum Recession: Causes, Treatment, Prevention

Gum recession, where the gums tissue around your teeth begins to move away from the teeth. It can occur in adults as well as children and teenagers who do not receive proper dental care early on. Gum recession can lead to the exposure of your teeth’s roots and the bone that surrounds them, which can cause pain and infection if not treated properly by a dentist or periodontist. To keep gum recession from occurring, practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly for checkups.
Reasons Behind It
Gum recession can be caused by a number of factors, including poor oral hygiene and receding gums. One cause of gum recession is trauma to your teeth, resulting in a crack in your tooth. The gum tissue can no longer hold itself in place and therefore starts to recede. Another possible cause of gum recession is grinding or clenching your teeth; over time, constant pressure on your teeth can loosen them and lead to exposure that may lead to oral problem. Certain medical conditions such as psoriasis can also contribute to gum recession. People with dry mouth syndrome may experience gum recession due to an insufficient amount of saliva for protection against bacteria. If you have periodontal disease, you are more likely to develop gum recession as well. Gum recession can be treated easily at home by brushing your teeth twice daily and flossing every day.
How To Treat It?
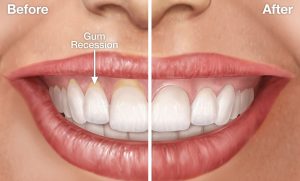
Treating gum recession can be done surgically or non-surgically. For example, a type of surgery called a flap procedure can be performed in which an oral surgeon lifts up gums to reattach them and bring them closer to the teeth. The success rate for these surgeries depends on many factors. Another surgical procedure involves stabilizing loose teeth with crowns; if stabilized, they act as anchors for surrounding gums to reattach themselves closer to the teeth. This also may help prevent future recession of gums around molars and premolars.
Nonsurgical treatments include orthodontics (braces), dental implants, bone grafts (adding bone around roots that have receded), and fillings that support neighboring teeth instead of relying on weaker nearby roots for support. If caught early enough, it can often be prevented by altering habits such as brushing too hard or using improper flossing techniques. Frequent dental visits are recommended to catch early signs of gums recession, such as puffy pink tissue around your gums or receding gums.
How Can You Prevent it?
The most important step in preventing this dental problem is making sure you’re brushing and flossing regularly. Regular brushing will help you maintain a healthy oral environment, but it’s more than just about scrubbing at your teeth for 2 minutes each morning. You need to use an electric toothbrush with a built-in timer to make sure you’re spending enough time properly brushing your teeth. Additionally, make sure that you are cleaning along your gumline on a regular basis; many people find that their gums begin receding because they aren’t taking their time cleaning below their gums. It can be difficult to get used to having clean gums again after neglecting them for so long – start off slow! Begin with flossing once per day and slowly increase from there as you become accustomed to maintaining healthier gums.